How much do we really understand about the different types of cholesterol, how high cholesterol can impact our health, and what we can do about mitigating the likelihood we develop high cholesterol? Many don’t, so we have put together a guide so you can better understand cholesterol, and make informed decisions for your well-being. To start, the liver produces 90% of the body’s cholesterol and does so while we sleep, while only 10% of cholesterol is derived from the foods we eat.
Cholesterol is an essential building block for the normal metabolism of the body. Cholesterol is a type of fat known as a lipid. Lipids cannot circulate alone in the bloodstream, they require a means of transportation. Water-soluble proteins, called lipoproteins transport cholesterol in the blood, and the amount of lipoprotein determines how much cholesterol can be moved. The three types of lipoproteins are:
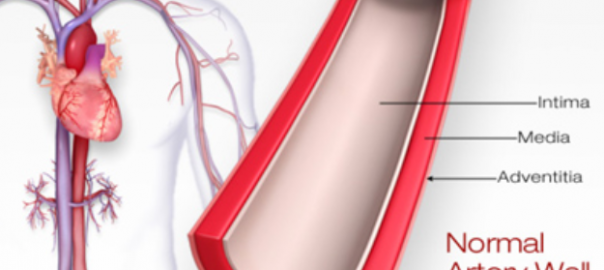
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) – This is casually known as “good” cholesterol because it removes cholesterol from arterial plaque and transports it back to the liver to be metabolized. If the plaque within an artery were to build to the point it begins to restrict the flow of blood to the heart, a heart attack may ensue.
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) – This is the “bad” cholesterol your doctor will warn you about because it deposits cholesterol into the inflamed plaque of the artery wall.
Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) – This lipoprotein is created by your liver to be released into the bloodstream and is considered “bad” for your health. It mainly carries triglycerides (another type of fat) to your tissues, and if we have this in high volumes, it can put us at risk for a stroke.
To calculate your cholesterol levels, your doctor will evaluate the sum of all three of these lipoproteins and your triglycerides to generate a lipid profile. Then, total cholesterol is divided by your high-density lipoprotein level, resulting in your cholesterol ratio number, and you want it to be low.
The implication of high cholesterol on your health is an increased risk that the fatty deposits along the walls of your artery or arteries clot, and cause a heart attack or stroke. While you may be able to survive a heart attack or stroke, it can be fatal. Thankfully, you can begin to restore the health of your arteries by incorporating heart-healthy foods into your diet, regularly exercising, drinking alcohol in moderation, losing weight, and quit smoking if you are someone who does smoke.
If you would like more information on cholesterol, contact Dr. Gordon C. Gunn MD at 714-912-2211 or visit www.gordongunnmd.com to schedule an appointment today.
Dr. Gordon Gunn proudly serves Fullerton and all surrounding areas.